Introduction
Roseomonas mucosa, which is a Gram-negative coccobacillus, is an opportunistic pathogen that has been rarely encountered in human infections.1 The genus Roseomonas is characterized as a pink-pigmented, oxidative, mucosal Gram-negative coccobacillus, that is mostly isolated from environmental samples, such as water, soil, air and plants.2 Roseomonas consisted of three named genomospecies, which were Roseomonas gilardii, R. cervicalis, and R. fauriae, and also three unnamed genomospecies.3 Currently, the genus Roseomonas constitutes 15 valid species, which includes R. aquatica, R. aerilata, R. cervicalis, R. gilardii, R. lacus, R. mucosa, R. terrae, R. stagni, R. vinacea, R. fauriae, and other unnamed genomospecies.4
Case Report
On 25th August 2022, a 15-year-old girl from Kochi, with no known comorbidity presented to the emergency department with history of fever, myalgia, erythematous rashes over palms, soles, inner aspect of both upper and lower limbs for 5 days, decreased urine output, breathlessness, loose stools, vomiting for 1 day. History of exposure to contaminated water was present. Patient was vaccinated up to age, but not vaccinated against Covid, with no significant past medical history.
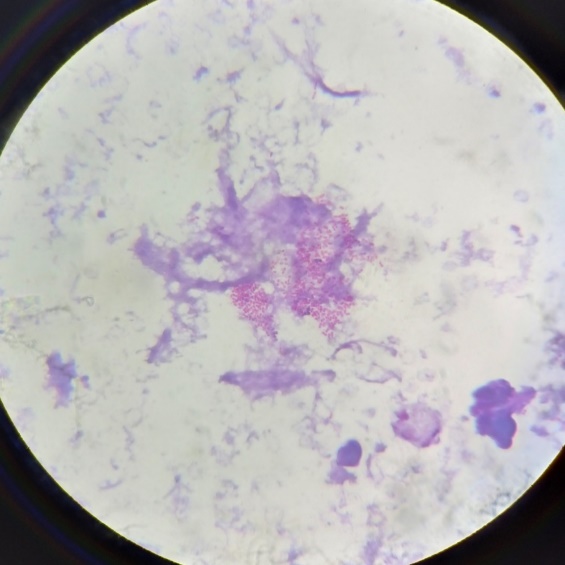
On examination, patient was conscious, oriented, tachypnoeic, hypotensive and had tachycardia. Erythematous maculopapular rashes were present over both palms. Other system examinations were within normal limits. Routine investigations showed normocytic normochromic anemia (Hb=9.1g/dL), neutrophilic leukocytosis, elevated inflammatory markers, deranged liver function and renal function. All clinical and investigation findings were suggestive of septic shock. CT chest showed bilateral patchy ground glass opacities with CT severity index of 11/25. Patient was tested Covid antibody positive, Covid RTPCR was negative, cardiac biomarkers were found to be elevated. Echocardiography showed LV apical and lateral wall hypokinesia and pericardial effusion, all features suggestive of viral myocarditis. Patient tested negative for tropical infections. Patient’s clinical and investigational parameters were suggestive of post Covid Multisystem inflammatory syndrome. Blood sample was sent for culture and sensitivity on the day of admission before starting antibiotics under aseptic precautions. Sample was inoculated into automated blood culture system (BacT Alert). The blood culture bottle flagged positive on the 4th day of incubation. The sample from this bottle was sub-cultured to Blood agar and MacConkey agar plates. Direct smear examination showed gram negative coccobacilli.(Figure 1)
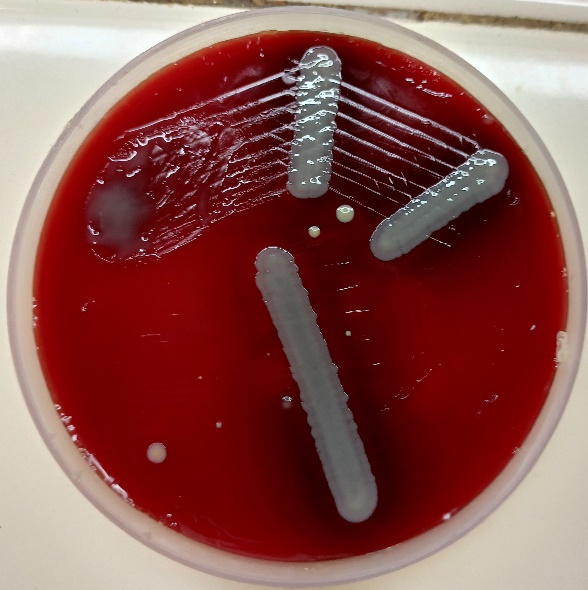
Both the culture plates showed no growth after 24 hours of incubation at 37°C, so were incubated further. After 48 hours, blood agar plate showed scanty growth of non-lytic grey mucoid colonies. Culture smear showed gram negative coccobacilli.(Figure 2)
The isolate tested catalase positive and oxidase negative. It was proceeded with biochemical reactions and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Even after 48 hours of incubation, no growth was detected in the biochemical tubes or antimicrobial sensitivity testing plates or subculture plates. VITEK 2 ID/ST was also put up with gram negative ID card and non fermenter (AST-N281) card. VITEK report came as non or low reactive bio pattern. VITEK MS was performed at a higher center where the isolate was identified as Roseomonas mucosa. Sputum culture showed normal pharyngeal flora and urine culture was sterile.
Patient was treated with meropenem, doxycycline and standard treatment protocol for septic shock. Patient showed steady improvement on the following days. Doxycycline was stopped after 5 days and meropenem was continued for total 14 days and patient was discharged.
Result
In our case the patient was immunocompromised, most likely due to post Covid illness. She had history of contact with contaminated water. Patient presented in septic shock. Blood culture yielded a slow growing gram negative coccobacilli which was subsequently identified by VITEK MS to be Roseomonas mucosa. She was managed effectively with appropriate broad spectrum antibiotic (meropenem) and other supportive measures. Patient recovered and was discharged.
Discussion
Roseomonas has been commonly found in the environment, including the soil, water, and air. The pathogenic mechanism and clinical significance of Roseomonas are not well understood. Studies suggest that Roseomonas can be present in turbid water from dirty or contaminated faucets.5 Roseomonas mucosa has low human pathogenicity but it can cause systemic infection in individuals with underlying diseases or immunocompromised patients.6 Cases have been reported in immunocompetent patients as well.7 These microbes cause central line-associated bloodstream infections, and also have the potential to cause respiratory, skin and soft tissue, peritoneal, and urinary tract infections, apart from spondylitis and subretinal abscesses.8
Members of this genus are nonfermentative, weakly staining, appear as gram-negative, plump coccoid rods, arranged in pairs or short chains, to mainly cocci with only occasional rods. They grow on 5% sheep blood agar, chocolate agar, buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE) agar, Sabouraud’s agar, and almost always (91%) on MacConkey agar. They can grow at 25°C, 35°C and usually 42°C. Growth appears as pale-pink, pinpoint, shiny, raised, and often mucoid colonies with entire margins after 2 to 3 days of incubation at 35°C. Roseomonas grow very well on Sabouraud’s agar, producing light pink mucoid (sometimes runny) colonies. The organisms do not appear black when viewed under UV light which helps to differentiate Roseomonas from Methylobacterium which do appear black under UV light. All strains are weakly oxidase positive (often after 30 seconds) or oxidase negative, catalase positive, and urease positive.9
Carbapenems, aminoglycosides, and tetracyclines are the most effective antibiotics against Roseomonas species. In general, these organisms have high MICs to penicillins and cephalosporins, with the exception of β-lactamase inhibitor combinations, which are frequently, but not invariably active. Roseomonas species usually have low MICs to fluoroquinolones but high MICs to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.10
Conclusion
Roseomonas is known to be an organism with low pathogenicity in humans. However, in immunocompromised persons, they can cause serious infections. The difficulty in identification by conventional methods further complicates the diagnosis. A high degree of suspicion and the availability of advanced diagnostic facilities can be of benefit in the detection of this rare pathogen.
Acknowledgement
Dr Joana Mary Magdaline, Professor and Head, Department of Microbiology, Government Medical College, Ernakulam. Dr Jacob K Jacob, Professor and Head, Department of General Medicine, Government Medical College, Ernakulam. Dr Sushitha T S, Assistant Professor, Department of Microbiology, Government Medical College, Ernakulam.